 BBC
BBCThe planet has moved a big step nearer to warming greater than 1.5C, new information presentations, in spite of global leaders vowing a decade in the past they might attempt to steer clear of this.
The Eu Copernicus local weather provider, one of the vital major world information suppliers, mentioned on Friday that 2024 used to be the primary calendar yr to go the symbolic threshold, in addition to the sector’s most up to date on file.
This doesn’t imply the world 1.5C goal has been damaged, as a result of that refers to a long-term moderate over a long time, however does convey us closer to doing in order fossil gas emissions proceed to warmth the ambience.
Final week UN leader António Guterres described the hot run of temperature data as “local weather breakdown”.
“We will have to go out this highway to break – and we don’t have any time to lose,” he mentioned in his New 12 months message, calling for nations to slash emissions of planet-warming gases in 2025.
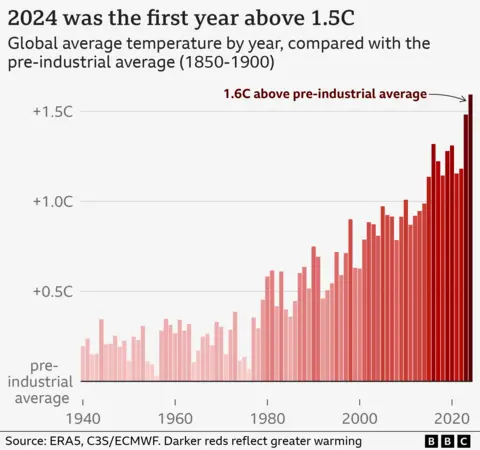
World moderate temperatures for 2024 have been round 1.6C above the ones of the pre-industrial duration – the time sooner than people began burning huge quantities of fossil fuels – in line with Copernicus information.
This breaks the file set in 2023 through simply over 0.1C, and way the final 10 years at the moment are the ten warmest years on file.
The Met Place of work, Nasa and different local weather teams are because of free up their very own information afterward Friday. All are anticipated to agree that 2024 used to be the warmest on file, even supposing actual figures range reasonably.
Final yr’s warmth is predominantly because of humanity’s emissions of planet-warming gases, equivalent to carbon dioxide, that are nonetheless at file highs.
Herbal climate patterns equivalent to El Niño – the place floor waters within the jap tropical Pacific Ocean turn out to be strangely heat – performed a smaller position.
“Through a ways and away the most important contribution impacting our local weather is greenhouse fuel concentrations within the surroundings,” Samantha Burgess, deputy director of Copernicus, tells the BBC.
The 1.5C determine has turn out to be an impressive image in world local weather negotiations ever because it used to be agreed in Paris in 2015, with most of the maximum susceptible nations taking into account it an issue of survival.
The hazards from local weather trade, equivalent to intense heatwaves, emerging sea-levels and lack of flora and fauna, could be a lot upper at 2C of warming than at 1.5C, in line with a landmark UN file from 2018.
But the sector has been transferring nearer and nearer to breaching the 1.5C barrier.
“When precisely we can go the long-term 1.5C threshold is tricky to are expecting, however we are clearly very shut now,” says Myles Allen of the Division of Physics on the College of Oxford, and an writer of the UN file.
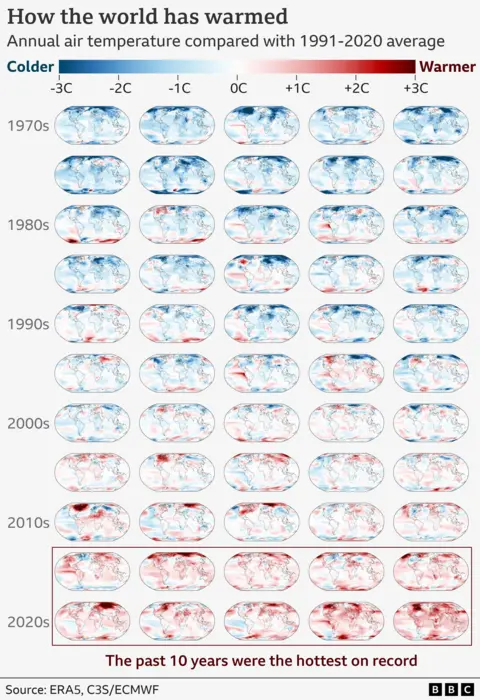
The present trajectory would most likely see the sector go 1.5C of long-term warming through the early 2030s. This might be politically important, nevertheless it would not imply recreation over for local weather motion.
“It isn’t like 1.49C is ok, and 1.51C is the apocalypse – each 10th of a point issues and local weather affects get step by step worse the extra warming we’ve got,” explains Zeke Hausfather, a local weather scientist at Berkeley Earth, a analysis staff in america.
Even fractions of a point of worldwide warming can convey extra common and intense excessive climate, equivalent to heatwaves and heavy rainfall.
In 2024, the sector noticed blistering temperatures in west Africa, extended drought in portions of South The us, intense rainfall in central Europe and a few in particular sturdy tropical storms hitting north The us and south Asia.
Those occasions have been only a few of the ones made extra intense through local weather trade during the last yr, in line with the International Climate Attribution staff.
Even this week, as the brand new figures are launched, Los Angeles has been beaten with damaging wildfires fuelled through top winds and a loss of rain.
Whilst there are lots of contributing components to this week’s occasions, professionals say stipulations conducive to fires in California are changing into much more likely in a warming global.
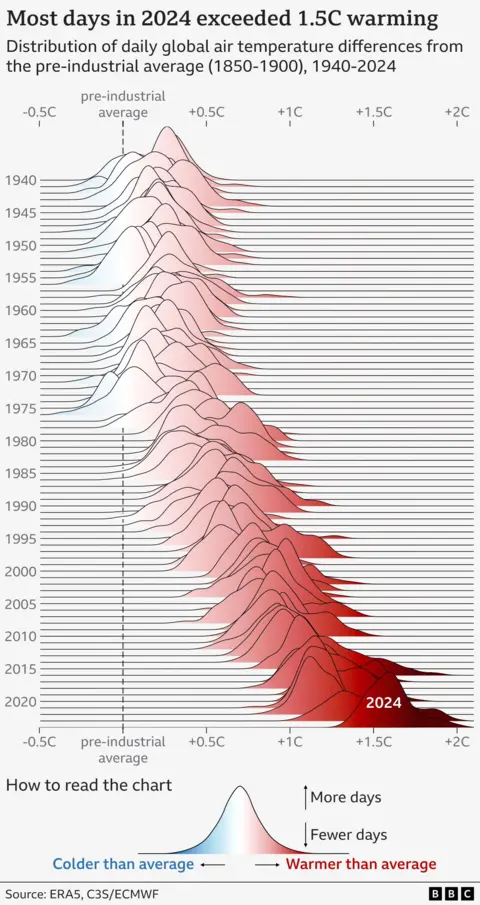
It wasn’t most effective air temperatures that set new marks in 2024. The global’s sea floor additionally reached a brand new day-to-day top, whilst the full quantity of moisture within the surroundings reached file phases.
That the sector is breaking new data isn’t a wonder: 2024 used to be at all times anticipated to be scorching, as a result of the impact of the El Niño climate trend – which ended round April final yr – on most sensible of human-caused warming.
However the margin of a number of data in recent times has been much less anticipated, with some scientists fearing it will constitute an acceleration of warming.
“I feel it is secure to mention that each 2023 and 2024 temperatures stunned maximum local weather scientists – we did not suppose we might be seeing a yr above 1.5C this early,” says Dr Hausfather.
“Since 2023 we’ve got had round 0.2C of additional warming that we will’t absolutely give an explanation for, on most sensible of what we had anticipated from local weather trade and El Niño,” consents Helge Gößling, a local weather physicist on the Alfred Wegener Institute in Germany
More than a few theories had been instructed to give an explanation for this ‘additional’ heat, equivalent to an obvious relief within the low-level cloud duvet that has a tendency to chill the planet, and extended ocean warmth following the top of El Niño.
“The query is whether or not this acceleration is one thing continual related to human actions that implies we can have steeper warming sooner or later, or whether or not it is part of herbal variability,” Dr Gößling provides.
“Nowadays it is very onerous to mention.”
Regardless of this uncertainty, scientists pressure that people nonetheless have regulate over the long run local weather, and sharp discounts in emissions can reduce the effects of warming.
“Even though 1.5 levels is out the window, we nonetheless can most likely prohibit warming to one.6C, 1.7C or 1.8C this century,” says Dr Hausfather.
“That is going to be a ways, a ways higher than if we stay burning coal, oil and fuel unabated and finally end up at 3C or 4C – it nonetheless truly issues.”





