 PNRA_IPEV
PNRA_IPEVWhat’s more than likely the sector’s oldest ice, courting again 1.2m years in the past, has been dug out from deep inside Antarctica.
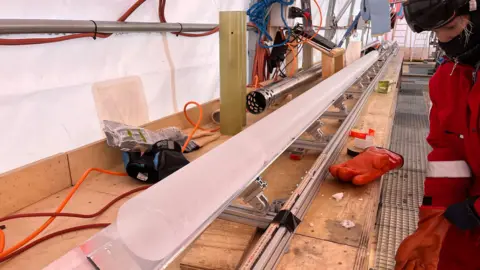
Operating at temperatures of -35C, a group of scientists extracted a 2.8km-long cyclinder, or core, of ice – longer than 8 Eiffel Towers end-to-end.
Suspended throughout the ice are historic air bubbles which scientists hope will lend a hand resolve a long lasting thriller about our planet’s local weather historical past.
The Ecu scientists labored over 4 Antarctic summers, racing towards seven international locations to be first to achieve the rock underneath the frozen continent.
 PNRA_IPEV
PNRA_IPEVTheir paintings may just lend a hand get to the bottom of some of the primary mysteries in our planet’s local weather historical past – what took place 900,000-1.2 million years in the past when glacial cycles have been disrupted and some researchers say our ancestors got here just about extinction.
“It is an important fulfillment,” says Prof Carlo Barbante at Ca’ Foscari College of Venice who co-ordinated the analysis.
“You might have for your palms a work of ice that may be a million years previous. Now and again you spot ash layers coming from volcanic eruptions. You spot the tiny bubbles inside of, some bubbles of air that our ancestors breathed one million years in the past,” he says.
The group used to be led by way of the Italian Institute of Polar Sciences and integrated 10 Ecu international locations.
 PNRA_IPEV
PNRA_IPEVIt needed to shipping the drilling apparatus, laboratories and camp 40km by way of snow mobiles from the closest analysis base.
The drilling web page, referred to as Little Dome C, is at the Antarctic plateau at the east of the continent, at virtually 3000m elevation.
Ice cores are a very important to scientists’ figuring out of the way our local weather is converting.
They lure bubbles of air and debris that expose ranges of greenhouse gasoline emissions and temperature variation that lend a hand scientists plot how climatic prerequisites have altered through the years.
Information from different ice cores, together with one referred to as Epica, helped scientists conclude that the present upward thrust in temperature connected to greenhouse gasoline emissions is led to by way of people burning fossil fuels.
 PNRA_IPEV
PNRA_IPEVHowever scientists sought after to head additional again in time.
Now with this undertaking Past Epica: Oldest Ice they’ve won doubtlessly any other 400,000 years of historical past.
“There’s numerous the previous in our long run. We have a look at the previous to grasp higher how the local weather works and the way are we able to undertaking it into the longer term,” says Prof Barbante.
The group had a “nail-biting previous few days” as they have been ready to drill even deeper than expected from radar knowledge, says Dr Robert Mulvaney, an ice core scientist at British Antarctic Survey.

The core used to be slowly pulled from the ice sheet the use of a drill equipment and scientists moderately wiped clean the ice the use of cloths.
It’s now being minimize into one metre items for transportation at -50C from Antarctica by way of boat.
The items will ultimately achieve the freezers of a large number of Ecu establishments, together with the British Antarctic Survey in Cambridge, the place scientists will start their research.
Mavens need to perceive what took place in a duration 900,000 to at least one.2 million years in the past referred to as the Mid-Pleistocene Transition.
At the moment, the period of the cycle between chilly glacial and heat interglacials switched from being 41,000 years to 100,000 years. However scientists have by no means understood why.
This is identical duration when, in accordance to a few theories, the ancestors of present-day people virtually died out, most likely losing to round simply 1000 people.
Scientists have no idea if there’s a hyperlink between this near-extinction and the local weather, explains Prof Barbante, nevertheless it demonstrates it’s an peculiar duration that it is very important higher perceive.
“What they’ll in finding is any one’s wager however it’s going to no doubt amplify our window on our planet’s previous,” Professor Joeri Rogelj from Imperial School in London, who used to be no longer concerned within the undertaking, instructed BBC Information.
Apply Georgina on BlueSky.





