Local weather and science reporter
Information journalist
 Getty Photographs
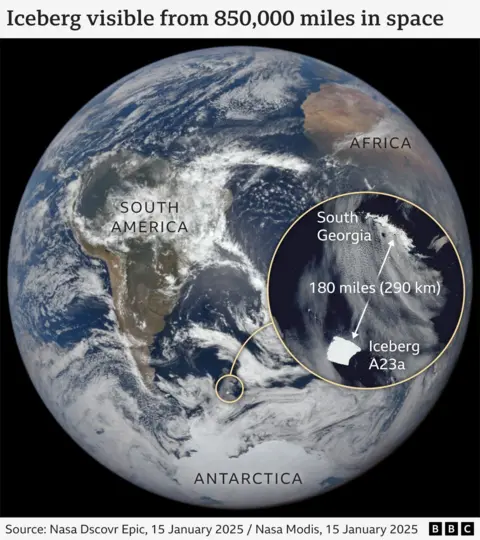
Getty PhotographsThe sector’s biggest iceberg is on a collision direction with a far off British island, doubtlessly hanging penguins and seals at risk.
The iceberg is spinning northwards from Antarctica against South Georgia, a rugged British territory and natural world haven, the place it might floor and spoil into items. It’s lately 173 miles (280km) away.
Numerous birds and seals died on South Georgia’s icy coves and seashores when previous massive icebergs stopped them feeding.
“Icebergs are inherently bad. I’d be extremely satisfied if it simply utterly neglected us,” sea captain Simon Wallace tells BBC Information, talking from the South Georgia govt vessel Pharos.
 BFSAI
BFSAIAround the globe a gaggle of scientists, sailors and fishermen are anxiously checking satellite tv for pc footage to watch the day-to-day actions of this queen of icebergs.
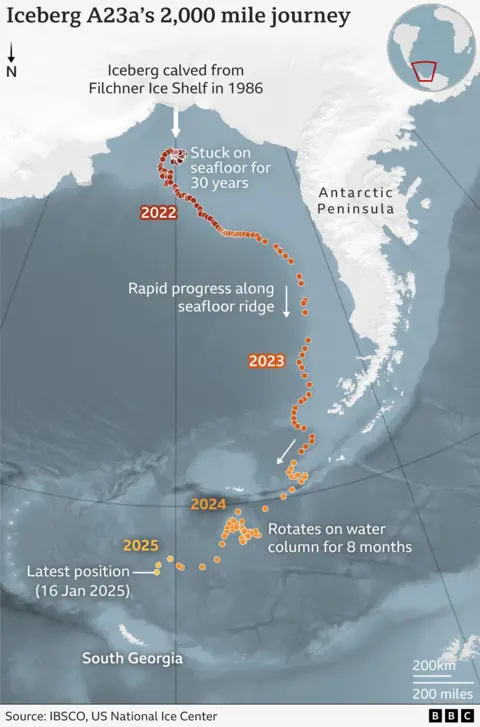
It’s referred to as A23a and is without doubt one of the global’s oldest.
It calved, or broke off, from the Filchner Ice Shelf in Antarctica in 1986 however were given caught at the seafloor after which trapped in an ocean vortex.
In spite of everything, in December, it broke unfastened and is now on its ultimate adventure, rushing into oblivion.
The hotter waters north of Antarctica are melting and weakening its huge cliffs that tower as much as 1,312ft (400m), taller than the Shard in London.
It as soon as measured 3,900 sq km, however the newest satellite tv for pc footage display it’s slowly decaying. It’s now round 3,500 sq km, more or less the scale of the English county of Cornwall.
And big slabs of ice are breaking off, plunging into the waters round its edges.
A23a may just wreck into huge segments any day, which would possibly then hang out for years, like floating towns of ice cruising uncontrollably round South Georgia.
This is not the primary large iceberg to threaten South Georgia and Sandwich Islands.
In 2004 one known as A38 grounded on its continental shelf, leaving useless penguin chicks and seal domestic dogs on seashores as large ice chunks blocked their get right of entry to to feeding grounds.
The territory is house to valuable colonies of King penguins and thousands and thousands of elephant and fur seals.
“South Georgia sits in iceberg alley so affects are to be anticipated for each fisheries and natural world, and each have a really perfect capability to evolve,” says Mark Belchier, a marine ecologist who advises the South Georgia govt.
Sailors and fisherman say icebergs are an expanding drawback. In 2023 one known as A76 gave them a scare when it got here on the subject of grounding.
“Chunks of it have been tipping up, so that they gave the look of nice ice towers, an ice town at the horizon,” says Mr Belchier, who noticed the iceberg whilst at sea.
The ones slabs are nonetheless lingering across the islands as of late.
“It’s in bits from the scale of a number of Wembley stadiums right down to items the scale of your table,” says Andrew Newman from Argos Froyanes, a fishing corporate that works in South Georgia.
“The ones items principally quilt the island – we need to paintings our approach thru it,” says Captain Wallace.
The sailors on his send should be continuously vigilant. “Now we have searchlights on all night time to check out to look ice – it may possibly come from nowhere,” he explains.
A76 used to be a “gamechanger”, in line with Mr Newman, with “large have an effect on on our operations and on preserving our vessel and group protected”.
 Simon Wallace
Simon WallaceAll 3 males describe a swiftly converting setting, with glacial retreat visual year-to-year, and risky ranges of sea ice.
Local weather trade is not likely to were at the back of the beginning of A23a as it calved goodbye in the past, earlier than a lot of the affects of emerging temperatures that we at the moment are seeing.
However massive icebergs are a part of our long run. As Antarctica turns into extra volatile with hotter ocean and air temperatures, extra huge items of the ice sheets will become independent from.
Earlier than its time involves an finish even though, A23a has left a parting reward for scientists.
A staff with the British Antarctic Survey at the Sir David Attenborough analysis vessel discovered themselves on the subject of A23a in 2023.
The scientists scrambled to milk the uncommon alternative to research what mega icebergs do to the surroundings.
 Tony Jolliffe/BBC
Tony Jolliffe/BBCThe send sailed right into a crack within the iceberg’s gigantic partitions, and PhD researcher Laura Taylor amassed valuable water samples 400m clear of its cliffs.
“I noticed a large wall of ice approach upper than me, so far as I may just see. It has other colors somewhere else. Chunks have been falling off – it used to be moderately magnificent,” she explains from her lab in Cambridge the place she is now analysing the samples.
Her paintings seems at what the have an effect on the soften water is having at the carbon cycle within the southern ocean.
 Getty Photographs
Getty Photographs“This is not simply water like we drink. It is stuffed with vitamins and chemical substances, in addition to tiny animals like phytoplankton frozen inside of,” Ms Taylor says.
Because it melts, the iceberg releases the ones parts into the water, converting the physics and chemistry of the sea.
That might retailer extra carbon deep within the ocean, because the debris sink from the skin. That might naturally lock away probably the most planet’s carbon dioxide emissions that give a contribution to local weather trade.
Icebergs are notoriously unpredictable and nobody is aware of what precisely it’ll do subsequent.
However quickly the behemoth must seem, looming at the islands’ horizons, as giant because the territory itself.






