 BBC
BBCOn Christmas Eve, an self sustaining spacecraft flew previous the Solar, nearer than any human-made object ahead of it. Swooping during the setting, Nasa’s Parker Sun Probe was once on a challenge to find extra in regards to the Solar, together with the way it impacts house climate at Earth.
This was once a landmark second for humanity – however one with none human at once concerned, because the spacecraft performed its pre-programmed duties on its own because it flew previous the solar, and not using a verbal exchange with Earth in any respect.
Robot probes were despatched around the sun machine for the final six a long time, attaining locations unattainable for people. Throughout its 10-day flyby, the Parker Sun Probe skilled temperatures of 1000C.
However the good fortune of those self sustaining spacecraft – coupled with the upward thrust of recent complex synthetic intelligence – raises the query of what function people would possibly play in long term house exploration.
 NASA
NASASome scientists query whether or not human astronauts are going to be wanted in any respect.
“Robots are growing rapid, and the case for sending people is getting weaker at all times,” says Lord Martin Rees, the United Kingdom’s Astronomer Royal. “I do not believe any taxpayer’s cash will have to be used to ship people into house.”
He additionally issues to the chance to people.
“The one case for sending people [there] is as an journey, an revel in for rich folks, and that are supposed to be funded privately,” he argues.
Andrew Coates, a physicist from College School London, concurs. “For severe house exploration, I a lot choose robotics,” he says. “[They] cross a lot additional and do extra issues.”
 NASA
NASAThey’re additionally inexpensive than people, he argues. “And as AI progresses, the robots may also be cleverer and cleverer.”
However what does that imply for long term generations of budding astronauts – and unquestionably there are particular purposes that people can do in house however which robots, on the other hand complex, by no means may?
Rovers verses mankind
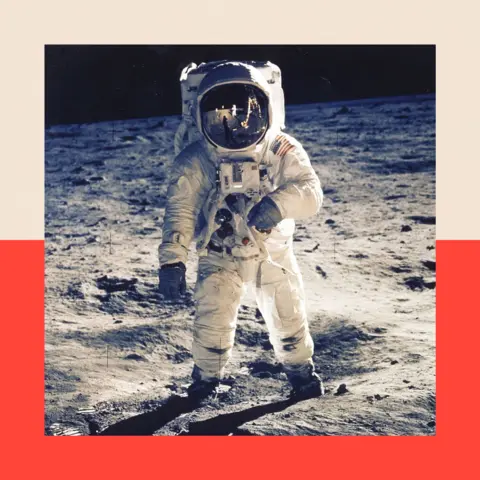
Robot spacecraft have visited each planet within the sun machine, in addition to many asteroids and comets, however people have most effective long gone to 2 locations: Earth’s orbit and the Moon.
In all, about 700 folks were to house, for the reason that earliest in 1961, when Yuri Gagarin from the then-Soviet Union turned into the primary cosmic explorer. Maximum of the ones were into orbit (circling the Earth) or suborbit (quick vertical hops into house lasting mins, on automobiles like the United States corporate Blue Starting place’s New Shepard rocket).
“Status will at all times be a explanation why that we’ve got people in house,” says Dr Kelly Weinersmith, a biologist at Rice College, Texas and co-author of A Town on Mars. “It sort of feels to were agreed upon as an effective way to turn that your political machine is efficacious and your persons are good.”
However apart from an innate want to discover, or a way of status, people additionally perform analysis and experiments in Earth’s orbit, corresponding to at the World House Station, and use those to advance science.
 NASA
NASARobots can give a contribution to that clinical analysis, being able to shuttle to places inhospitable to people, the place they may be able to use tools to check and probe the atmospheres and surfaces.
“People are extra flexible and we get stuff executed quicker than a robotic, however we are truly exhausting and dear to stay alive in house,” says Dr Weinersmith.
In her 2024 Booker Prize-winning novel Orbital, writer Samantha Harvey places it extra lyrically: “A robotic has little need for hydration, vitamins, excretion, sleep… It desires and asks for not anything.”
However there are downsides. Many robots are sluggish and methodical – for instance on Mars, the rovers (remote-controlled motor automobiles) trundle alongside at slightly 0.1mph.
“AI can beat human beings at chess, however does that imply they’re going to have the ability to beat human beings in exploring environments?” asks Dr Ian Crawford, a planetary scientist on the College of London. “I simply do not suppose we all know.”
He does, on the other hand, imagine that AI algorithms would possibly permit rovers to be “extra environment friendly”.
AI assistants and humanoid robots
Generation can play a component in complementing human house shuttle by way of liberating up astronauts from positive duties so they can center of attention on extra vital analysis.
“[AI could be used to] automate tedious duties,” explains Dr Kiri Wagstaff, a pc and planetary scientist in the United States who in the past labored at Nasa’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California. “At the floor of a planet, people get drained and lose center of attention, however machines may not.”
The problem is that massive quantities of energy are had to perform techniques like huge language fashions (LLM), which will perceive and generate human language by way of processing huge quantities of textual content knowledge. “We don’t seem to be on the level of having the ability to run an LLM on a Mars rover,” says Dr Wagstaff.
“The rovers’ processors run at a couple of 10th [of the speed] that your smartphone has” – that means they’re not able to deal with the serious calls for of working an LLM.
Advanced humanoid machines with robot hands and limbs are any other type of generation that would tackle elementary duties and purposes in house, specifically as they extra carefully mimic the bodily functions of people.
 NASA
NASANasa’s Valkyrie robotic was once constructed by way of the Johnson House Heart to compete in a 2013 robotics problem trial. Weighing 300lb and status at 6ft2in, it appears to be like now not not like a Big name Wars Stormtrooper, however it’s one in every of increasingly human-like machines with superhuman skills.
Lengthy ahead of the Valkyrie was once created, Nasa’s Robonaut was once the primary humanoid robotic designed to be used in house, taking over duties that have been differently carried out by way of people.
Its specifically designed palms supposed it will use the similar gear as astronauts and perform complicated, refined duties like greedy gadgets or flicking switches, that have been too difficult for different robot techniques.
A later type of the Robonaut was once flown to the World House Station at the house commute Discovery in 2011, the place it helped with upkeep and meeting.
 Reuters
Reuters“If we want to alternate an element or blank a sun panel, shall we do this mechanically,” says Dr Shaun Azimi, lead of the dexterous robotics group at Nasa’s Johnson House Heart in Texas. “We see robots with the intention to safe those habitats when people are not round.”
He argues that robots may well be helpful, to not change human explorers however to paintings along them.
Some robots are already running on different planets with out people, on occasion even making choices on their very own. Nasa’s Interest rover, for instance, is exploring a area known as Gale Crater on Mars and autonomously plays a few of its science with out human enter.
“You’ll be able to direct the rover to take footage of a scene, search for rocks that would possibly are compatible science priorities for the challenge, after which autonomously fireplace its laser at that focus on,” says Dr Wagstaff.
“It will possibly get a studying of a selected rock and ship it again to Earth whilst the people are nonetheless asleep.”
 NASA
NASAHowever the functions of rovers like Interest are restricted by way of their sluggish tempo. And there’s something else they can’t compete with too. This is, people have the added bonus of inspiring folks again on Earth in some way that machines can’t.
“Inspiration is one thing this is intangible,” argues Prof Coates.
Leroy Chiao, a retired Nasa astronaut who went on 3 flights to house within the Nineties and 2000s on Nasa’s House Commute and to the World House Station, concurs. “People relate when people are doing one thing.
“Most people is serious about robot missions. However I might be expecting the primary human on Mars to be even larger than the primary Moon touchdown.”
Lifestyles on Mars?
People have now not travelled additional than Earth’s orbit since December 1972, when the final Apollo challenge visited the Moon. Nasa is hoping to go back people there this decade with its Artemis programme.
The subsequent crewed challenge will see 4 astronauts fly across the Moon in 2026. An extra challenge, scheduled for 2027, will see Nasa astronauts land at the Moon’s floor.
 Reuters
ReutersThe Chinese language house company, in the meantime, additionally desires to ship astronauts to the Moon.
In different places Elon Musk, CEO of the United States corporate SpaceX, has his personal plans associated with house. He has stated that his long-term plan is to create a colony on Mars, the place people may land.
His thought is to make use of Starship, an unlimited new car that his corporate is growing, to move as much as 100 folks there at a time, with the purpose for there to be one million folks on Mars in two decades.
“Musk is arguing we want to transfer to Mars as a result of that may be a backup for humanity if one thing catastrophic occurs on Earth,” explains Dr Weinersmith. “If you are going to buy that argument, then sending people into house is vital.”
Then again, there are huge unknowns about residing on Mars, together with myriad technical demanding situations that she says stay unsolved.
“Perhaps small children cannot broaden in that atmosphere,” she says. “There [are] moral questions [like this] that we should not have the solutions to.
“I believe we will have to be slowing down.”
Lord Rees has a imaginative and prescient of his personal, even though, through which human and robot exploration would possibly merge to the purpose that people themselves are part-machine to deal with excessive environments. “I will believe they are going to use the entire tactics of genetic amendment, cyborg add-ons, and so forth, to deal with very adversarial environments,” he says.
“We could have a brand new species that shall be glad to live to tell the tale Mars.”
Till then, on the other hand, people are prone to proceed their small steps into the cosmos, on a trail lengthy trodden by way of robot explorers ahead of them.
Best symbol credit score: NASA
BBC InDepth is the brand new house at the web page and app for the most productive research and experience from our best newshounds. Underneath a particular new emblem, we’re going to convey you contemporary views that problem assumptions, and deep reporting at the largest problems that will help you make sense of a posh international. And we’re going to be showcasing thought-provoking content material from throughout BBC Sounds and iPlayer too. We are beginning small however considering giant, and we wish to know what you suppose – you’ll be able to ship us your comments by way of clicking at the button under.





