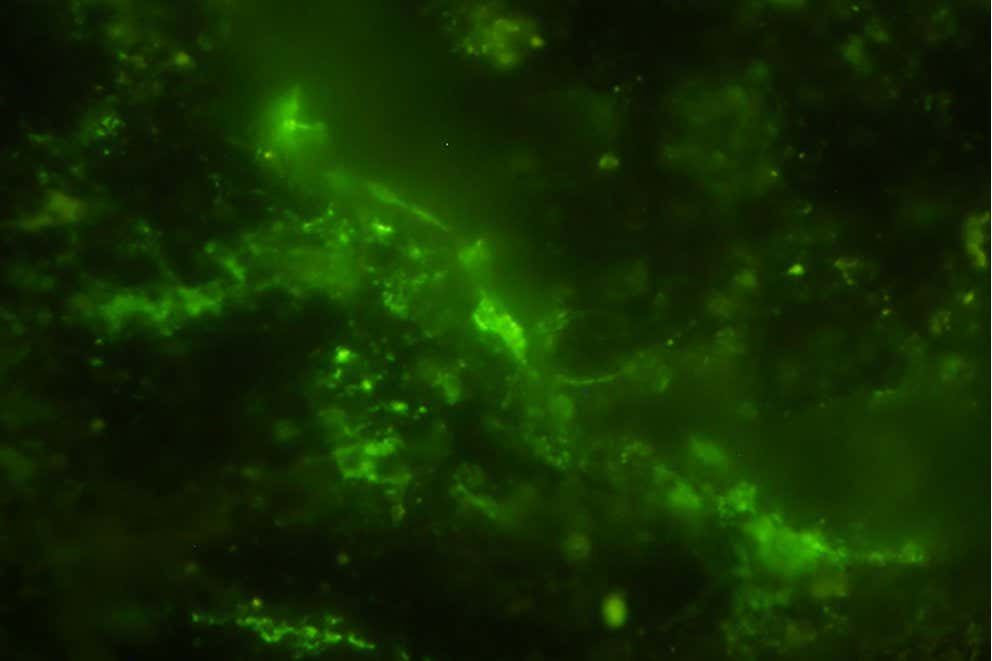
Cells discovered within historic rocks, their DNA stained with a inexperienced fluorescent dye
Y. Suzuki, S. J. Webb, M. Kouduka et al. 2024/ Microbial Ecology
Microorganisms had been discovered residing in tiny cracks inside a 2-billion-year-old rock in South Africa, making this the oldest identified rock to host existence. The invention may be offering new insights into the origins of existence on Earth and will even information the seek for existence past our planet.
We already knew that deep inside Earth’s crust, a long way got rid of from daylight, oxygen and meals assets, billions of resilient microorganisms live on. Dwelling in excessive isolation, those slow-growing microbes divide at a glacial tempo, now and again taking hundreds and even hundreds of thousands of years to finish cellular department.
“To this point, the oldest rocks wherein microbes had been discovered are 100-million-year-old seafloor sediments,” says Yohey Suzuki on the College of Tokyo. “We realize it’s conceivable that microbes can develop the use of one thing in those historic rocks.”
Now, Suzuki and his colleagues have driven that report again through just about 2 billion years. They received a 30-centimetre-long cylindrical rock core from 15 metres beneath the outside of the Bushveld Igneous Complicated in north-eastern South Africa, an unlimited formation of volcanic rock that shaped greater than 2 billion years in the past. Once they sliced open the core, they found out microbial cells residing within the rock’s tiny fractures.
The crew stained the microbes’ DNA and imaged them with a scanning electron microscope and fluorescent microscopy, then when compared them to possible contaminants to substantiate they have been indigenous to the rock pattern. Additionally they famous that the cellular partitions of the microbes have been nonetheless intact – an indication the cells have been alive and energetic.
“Have you ever noticed rocks from a volcano? Do you suppose the rest can reside in the ones rocks?” says Suzuki. “I without a doubt didn’t, so I used to be very excited after we discovered the microbes.”
The crew thinks the microorganisms have been carried into the rock by means of water in a while after its formation. Through the years, the rock was once clogged up through clay, which will have equipped the essential vitamins for the microorganisms to continue to exist.
“The microbes in those deep rock formations are very primitive in evolutionary phrases,” says Suzuki, who now hopes to extract and analyse their DNA to be told extra about them. Working out those historic organisms may provide clues about what the earliest sorts of existence on Earth will have gave the look of and the way existence advanced over the years.
This discovery may additionally have vital implications for the seek for existence on different planets. “The rocks within the Bushveld Igneous Complicated are similar to Martian rocks, particularly relating to age,” says Suzuki, so it’s conceivable that microorganisms might be persisting underneath the outside of Mars. He believes that making use of the similar method to differentiate between contaminant and indigenous microbes in Martian rock samples may lend a hand come across existence at the Pink Planet.
“This find out about provides to the view that the deep subsurface is the most important setting for microbial existence,” says Manuel Reinhardt on the College of Göttingen, Germany. “However the microorganisms themselves don’t seem to be 2 billion years outdated. They colonised the rocks after formation of cracks; the timing nonetheless must be investigated.”
Subjects: