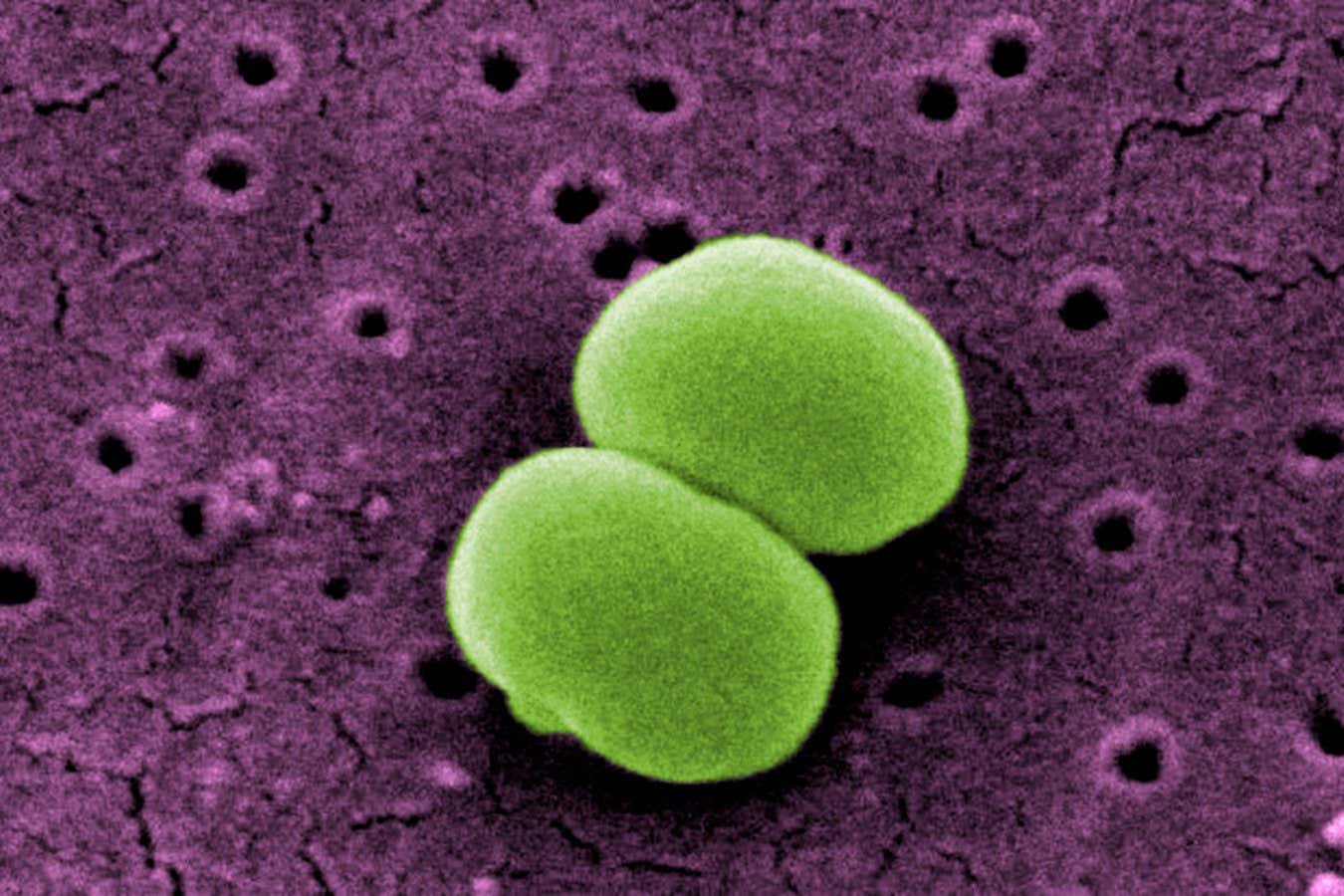
Staphylococcus epidermidis micro organism can input the frame by the use of pores and skin wounds
Scott Camazine/Alamy
A patch that zaps the surface with electric pulses might be used sooner than or after surgical treatment to stop micro organism at the pores and skin from inflicting blood poisoning, decreasing our reliance on antibiotics.
Staphylococcus epidermidis micro organism most often are living harmlessly on human pores and skin, but when they input the frame after surgical treatment or by the use of pores and skin cracks because of stipulations comparable to psoriasis, they are able to reason bloodstream infections, which may end up in dangerously low blood force.
Antibiotics can save you and deal with those infections, however this has resulted in antibiotic-resistant lines of S. epidermidis rising. In search of any other way, Bozhi Tian on the College of Chicago and his colleagues thought to be the potential for electric pulses, that have in the past been proven to kill micro organism.
The researchers created sq. plastic patches that had been 1 millimetre huge, each and every containing gold electrodes that, when stressed out up, produce electric pulses that may’t be felt by means of other people. They then unfold a pressure of S. epidermidis onto 5 samples of disinfected pig pores and skin and put a patch on most sensible of each and every piece.
After zapping the surface for 10 seconds each and every 10 mins for 18 hours, the workforce discovered that S. epidermidis ranges had been decreased 10-fold on those samples in comparison with others that had patches placed on them, however that didn’t ship electric pulses.
The intervention additionally disrupted the power of the micro organism to sign up for as much as shape a layer referred to as a biofilm, which has been connected to extra critical infections.
The consequences recommend that the patches, which might theoretically be reduce to any dimension, may just cut back the chance of significant drug-resistant S. epidermidis infections, says Tian.
In style antibiotic use is using an building up in drug resistance and this selection way may just assist sluggish the disaster, says Munehiro Asally on the College of Warwick, UK. However it’s unclear how the patches would possibly have an effect on different micro organism at the pores and skin that may additionally reason blood poisoning, he says.
Tian’s workforce plans to discover this in additional research and with a bit of luck take a look at the way on are living animals in a few yr.
Subjects: